point-of-care hemoglobin a1c testing a budget impact analysis|Impact of Point of Care Hemoglobin A1c Testing on Time to : distribution HbA 1c was assessed using a finger prick blood sample and analyzed with a point . WEB25 de jan. de 2018 · Thankfully, UnlimApps updated all these apps just in time to make them compatible with iOS 11. Apart from that, you can use these apps without revokes and with fully functional push notifications. The reason behind their incompatibility was the uasharedtools package. This package also received an update for iOS 11 and ensures .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 4600 Edmundson Rd. St. Louis, MO 63134. 314-733-8000. At Ascension, our commitment to patients and families begins with the doctors, nurses and care teams serving in our hospitals and care sites across the country. Our Catholic identity and healing Mission call us to care for everyone with dignity and .
Testing HbA1c where patients receive their diabetes care may improve system efficiency if the results from point-of-care HbA1c testing are comparable to those from laboratory HbA1c measurements. Objectives: To estimate the budget impact of point-of-care HbA1c .
HbA 1c was assessed using a finger prick blood sample and analyzed with a point .
This study showed that using POC-A1c devices in primary care settings is a cost .Point-of-care testing (POCT) for HbA1c provides a quick, easy, reliable method . The objective of this analysis was to estimate the budget impact (2013/2014) of point-of-care hemoglobin A 1c (POC HbA 1c) testing to replace laboratory hemoglobin A 1c .This analysis compared the average testing cost of 3 point-of-care HbA1c devices licensed by Health Canada and available on the market in Canada (Bayer’s A1cNow+, Siemens’s DCA .
The Impact of Point
To estimate the budget impact of point-of-care HbA1c testing to replace laboratory HbA1c measurement for monitoring glycemic control in patients with diabetes in .
Replacing all laboratory HbA1c measurements with point-of-care HbA1c testing would save approximately .7 million over the next year. Savings could be realized by the . Point-of-care testing (POCT) for HbA1c provides a quick, easy, reliable method for monitoring diabetes in the primary care office setting. The objectives of this quality improvement study were to evaluate the impact of .
Replacing laboratory HbA1c measurement with point-of-care HbA1c testing or using point-of-care HbA1c testing in combination with laboratory HbA1c measurement to monitor glycemic control .Without compromising accuracy, point of care testing (POCT) provides immediate results at the time of in person patient consultation. The purpose of this study was to evaluate time until .
Point
Point-of-care testing (POCT) for HbA1c provides a quick, easy, reliable method for monitoring diabetes in the primary care office setting. The objectives of this quality improvement study .
This study showed that using POC-A1c devices in primary care settings is a cost-effective alternative for monitoring glycated hemoglobin A1c as a marker of blood glucose .A total of 94 POCT HbA1c tests were included in the primary analysis. For the POCT HbA1c, the mean time to therapeutic intervention was 1.663.14hours. . Blackhouse G, Goeree R. Point-of-care hemoglobin A1c testing: a budget impact analysis. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser 2014;14:1–23. 204. 2. Pillay S, Aldous CM, Singh D, Pillay D . This analysis compared the average testing cost of 3 point-of-care HbA1c devices licensed by Health Canada and available on the market in Canada, with that of the laboratory Hb a1c reference method, to estimate the budget impact of point-a-1c testing to replace laboratory Ha1c measurement for monitoring glycemic control in patients with diabetes in 2013/2014. . Glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) testing plays a key role in the management of diabetes. 6 Guidelines on HbA1c testing frequency and treatment modifications aim at supporting the achievement of glycemic .
Impact of Point of Care Hemoglobin A1c Testing on Time to
The College of American Pathologists (CAP) also conducts biannual proficiency testing of A1C instruments ().Contrary to the NGSP annual certification, which demonstrates accuracy under optimal and standardized conditions, the CAP glycohemoglobin (GH2) survey provides information about accuracy and precision when assay methods are used in clinical . Assay standardization has markedly improved the accuracy and consistency of A1C testing. Devices to measure A1C at point of care (POC) are commercially available, allowing rapid results when the patient is seen. In this review, we describe how standardization of A1C testing was achieved, leading to high-quality results in clinical laboratories.
Without compromising accuracy, point of care testing (POCT) provides immediate results at the time of in person patient consultation. The purpose of this study was to evaluate time until therapeutic intervention with POCT HbA1c versus venipuncture, where venipuncture was considered standard of care.The primary outcome was time (hours) to implementation of a .Background: The hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is a gold-standard test to diagnose and monitor diabetes mellitus and has been incorporated into population health performance metrics for quality care. However, patients and practices remain challenged in completing timely HbA1c tests. Point-of-care testing (POCT) for HbA1c provides a quick, easy, reliable method for monitoring .
Background. The increasing prevalence of diabetes in Ontario means that there will be growing demand for hemoglobin A 1c (HbA 1c) testing to monitor glycemic control for the management of this chronic disease.Testing HbA 1c where patients receive their diabetes care may improve system efficiency if the results from point-of-care HbA 1c testing are .
Background:Point-of-care (POC) hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) testing has advantages over laboratory testing, but some questions have remained regarding the accuracy and precision of these methods. . Chadee A, Blackhouse G, Goeree R. Point-of-care hemoglobin A1c testing: a budget impact analysis. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. . The hemoglobin A1c (glycated hemoglobin, glycosylated hemoglobin, HbA1c, or A1c) test is used to evaluate a person's level of glucose control. The test shows an average of the blood sugar level over the past 90 days and represents a percentage. . Due to the variability of capillary point of care testing, any A1c done by capillary sample . A 2019 study reported that clinic-collected POC HbA 1c test values were a mean of 0.2 percentage points lower than the laboratory test values. 5 POC HbA 1c testing should not be used to establish a diagnosis of diabetes unless the test is validated as accurate and is subject to regular monitoring of its accuracy in clinical settings. 1,6 .Patzer K, Ardjomand P, Göhring K et al. Implementation of HbA1c Point of Care Testing in 3 German Medical Practices: Impact on Workflow and Physician, Staff, and Patient Satisfaction. J Diabetes Sci Technol.2018;12:687-694. Laurence CO, Gialamas A, Bubner T et al. Patient satisfaction with point-of-care testing in general practice.
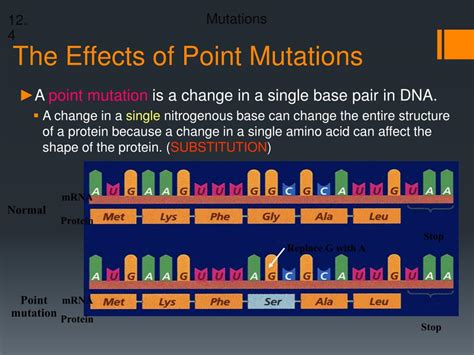
This analysis compared the average testing cost of 3 point-of-care HbA1c devices licensed by Health Canada and available on the market in Canada, with that of the laboratory Hb a1c reference method, to estimate the budget impact of point-a-1c testing to replace laboratory Ha1c measurement for monitoring glycemic control in patients with diabetes . Search life-sciences literature (Table 7: Budget Impact of POC HbA1c Testing - "Point-of-Care Hemoglobin A1c Testing: A Budget Impact Analysis." One of the 62 subjects had out-of-range HbA1c values and was excluded from analysis. The remaining 61 subjects each provided six fingerstick samples. . Goeree R. Point-of-care hemoglobin A1c testing: a budget impact analysis. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2014; 14:1-23. [PMC free article] . Three of 7 hemoglobin A1c point-of-care .
Cost

The practical impact of the current research is expected to be seen in . A systematic review and meta-analysis of test accuracy studies. Curr. Opin. . Christensen N.G., Sandberg S. Diagnosing diabetes mellitus: Performance of hemoglobin a1c point-of-care instruments in general practice offices. Clin. Chem. 2013;59:1790–1801. doi: 10.1373 . Background:Point-of-care (POC) hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) testing has advantages over laboratory testing, but some questions have remained regarding the accuracy and precision of these methods. . Chadee, A, Blackhouse, G, Goeree, R. Point-of-care hemoglobin A1c testing: a budget impact analysis. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. .
Clinical testing is an essential part of the health care process and is utilized primarily to give insight into a patient’s condition. In addition, testing will indicate what choices a physician should make in order to benefit a patient and help to modify their therapy in response to fluctuating disease states. In diabetes diagnosis and monitoring one of the primary tests .
A1C testing is recommended by the American Diabetes Association as a secondary measure of glycemic control in pregnant patients. Objective: To determine the utility of A1C point-of-care testing (POCT) during pregnancy to facilitate rapid counseling and diabetes care, particularly in relatively low-income transient patient populations. The growing endemics of diabetes and prediabetes, estimated to affect 10% and 30% of the adult population, respectively, highlight the need for effective and reliable methods for disease monitoring and management. 1 Left unmanaged or undermanaged, diabetes can lead to serious and costly complications, including cardiovascular and neurovascular disease, kidney . The growing endemics of diabetes and prediabetes, estimated to affect 10% and 30% of the adult population, respectively, highlight the need for effective and reliable methods for disease monitoring and management. 1 Left unmanaged or undermanaged, diabetes can lead to serious and costly complications, including cardiovascular and neurovascular disease, kidney .
Enhanced Document Preview: TRAINING SESSION FOR HBG A1C POCT Kyla Hoag NHS-FPX6004 Mary Burke May 07, 2023. PRESENTATION OUTLINE • Need for policy • What is point-of-care testing? • Policy's impact • Practice Guidelines • Role of Clinical Staff • Importance of New Policy NEED FOR POLICY • Failure to comply with national and state .The objective of this analysis was to review the correlation between point-of-care hemoglobin A 1c (POC HbA 1c) testing and laboratory hemoglobin A 1c (lab HbA 1c) measurement in patients with diabetes in clinical settings. Clinical Need and Target Population Description of Disease/Condition
The Pearson correlation between POC and the laboratory analysis test results was 0.884 ( P < .001). POC test sensitivity was 81.8% and specificity was 93.2%. . Impact of Point of Care Hemoglobin A1c Testing on Time to Therapeutic Intervention. Impact of COVID-19 on Chronic Ambulatory-Care-Sensitive Condition Emergency Department Use Among .
Introduction. The main objective of the current study was to perform a comparison of point-of-care testing for hemoglobin A1c (POCT-HbA1c) versus the standard laboratory method (Lab HbA1c) and their relationship to time-in-range (TIR) and glucose variability (GV) among patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) presented to the outpatient diabetes clinics.Hemoglobin A 1c is a blood test that measures the average blood sugar level over the past three months. Patients with diabetes should have hemoglobin A 1c levels tested every three to six months. In Ontario, most patients with diabetes go to community laboratories or hospitals for hemoglobin A 1c testing before their doctor appointments.. Health Quality Ontario Reviews .
Transfercar Brasil - Carros de realocação no Brasil - Transfer.
point-of-care hemoglobin a1c testing a budget impact analysis|Impact of Point of Care Hemoglobin A1c Testing on Time to